Glycoproteomics with FragPipe
FragPipe has several workflows for analyzing LC-MS/MS data of intact glycopeptides that provide a variety of capabilities and options. Glyco searches use the following tabs/tools in FragPipe:
- MSFragger-Glyco search: identifies candidate PSMs as a peptide sequence and total glycan mass
- Validation (Philosopher): PSM/protein FDR, filters to confident peptide sequence identifications
- PTM-Shepherd Glycan Composition Assignment: matches glycan mass to a single glycan composition with FDR control (not needed if using O-Pair)
- O-Pair: deconvolutes and localizes O-glycans from electron-based activation MS2 scans
There are several template glyco workflows (described in the workflows section) for a variety of search types and instrument activation methods. This tutorial covers each step of the process starting from loading raw data to validation and quantation of the results.
Glycoproteomics results can be viewed using the integrated FP-PDV viewer, Skyline, or directly from the psm.tsv results table(s) (see Examine the results for details). If glycan composition assignment or O-Pair search have been performed, there will be glyco-specific columns in the psm.tsv, including the Total Glycan Composition assigned. If only MSFragger search has been done, glycans will only appear as masses in the Delta Mass column. Make sure you are looking in the right place for the glycans depending on the type of search performed!
Example Glycoproteomics Analysis
For new users, we recommend working through this example, which walks through the complete glyco pipeline for an example dataset. The of this tutorial page describes the parameters and options for glyco workflows in general, and can be referenced while working through the example. https://fragpipe.nesvilab.org/docs/tutorial_glyco_example.html
Tutorial contents
- Load the data
- Load a glyco workflow template
- Load Protein and Glycan Databases
- Customize the search settings in MSFragger and Philosopher
- Customize the glycan identification and FDR settings in PTM-Shepherd
- Customize the O-Pair localization settings
- Set the output location and run
- Examine the results
Open FragPipe
When you launch FragPipe, check that MSFragger and Philosopher are both configured. If you haven’t downloaded them yet, use their respective ‘Download / Update’ buttons. See this page for more help. Python is not needed for glycoproteomics workflows.
Load the data
On the Workflow tab, load the data files to analyze (drag and drop or browse). Specify experiments if needed for the quantitation being done (not needed for most workflows). See this page for additional details on how to load and categorize experiment files.
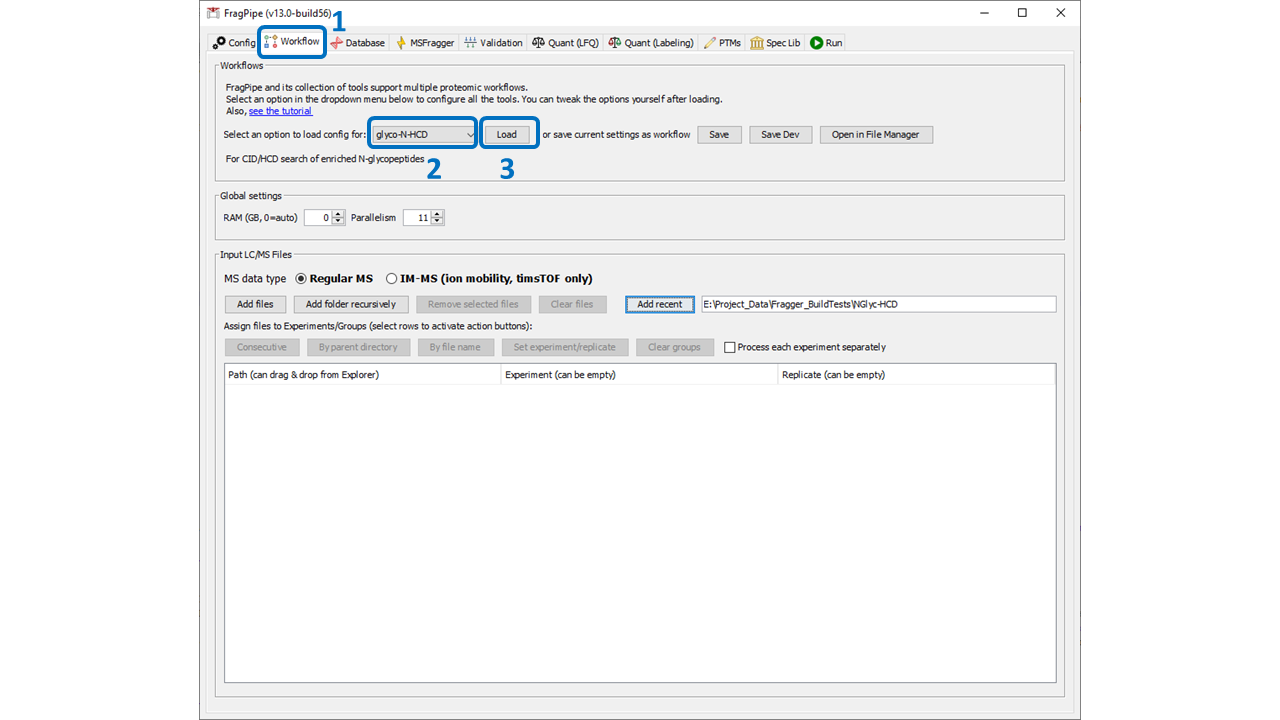
Load a Glyco workflow
Select the appropriate glyco workflow from the dropdown menu and click ‘Load’. There are pre-built workflows for N- and O-glycopeptide analyses with a variety of fragmentation and quantitation methods. See below for more details on the best workflow to choose. Loading a workflow sets the parameters to good base settings, but individual parameters may need to be updated for your analysis (described in this section). Please note: workflows come with a default set of human glycans. Don’t forget to load a glycan database that is appropriate for your analysis!
Workflows (organized by category):
Basic Workflows (template settings for different glycan types, activation types, and offset or open search)
glyco-N-HCD: Base workflow for identifying N-glycopeptides with CID/HCD fragmentation (no quant)
glyco-N-Hybrid: Glycopeptide identification for hybrid fragmentation (EThcD, AI-ETD, etc.) of N-glycopeptides
glyco-N-open-HCD: Open search (allowing unknown glycan masses) for CID/HCD fragmentation of N-glycopeptides
glyco-N-open-Hybrid: Open search (allowing unknown glycan masses) for hybrid fragmentation of N-glycopeptides
glyco-O-HCD: Glycopeptide identification for CID/HCD fragmentation of O-glycopeptides
glyco-O-Hybrid: Glycopeptide identification for hybrid fragmentation (EThcD, AI-ETD, etc.) of O-glycopeptides
glyco-O-open-HCD: Open search (allowing unknown glycan masses) for CID/HCD fragmentation of O-glycopeptides
glyco-O-open-Hybrid: Open search (allowing unknown glycan masses) for hybrid fragmentation of O-glycopeptides
glyco-O-Pair: Uses O-Pair to localize O-glycans instead of PTM-Shepherd composition assignment. Requires electron-based activation scan (either paired scans or single EThcD or EAD scan)
Workflows with Quant (Can be combined with settings from the Basic workflows to make quantitative workflows for any activation mode, but not open searches)
glyco-N-TMT: TMT quantitation of CID/HCD fragmented N-glycopeptides. Note: for TMT-quant of other fragmentation modes, start here and change fragmentation settings accordingly
glyco-N-LFQ: Label-free (MS1) quantation of CID/HCD fragmented N-glycopeptides
glyco-N-DIA: (experimental) library-based DIA quantation of CID/HCD fragmented N-glycopeptides. Requires DDA data to build a library.
glyco-O-DIA-OPair: (experimental) library-based DIA quantation of O-glycopeptides using OPair for site assignment with paired scan DDA data.
glyco-O-DIA-HCD: (experimental) library-based DIA quantation of CID/HCD fragmented O-glycopeptides with no site assignment. Glycans are placed on first allowed residue in the peptide.
Load Protein and Glycan Databases
Protein Sequence Database The protein sequence database is specified on the Database tab. Use the Download or Browse options to choose the appropriate database for your analysis. See the Specifying a protein sequence database tutorial for more details.
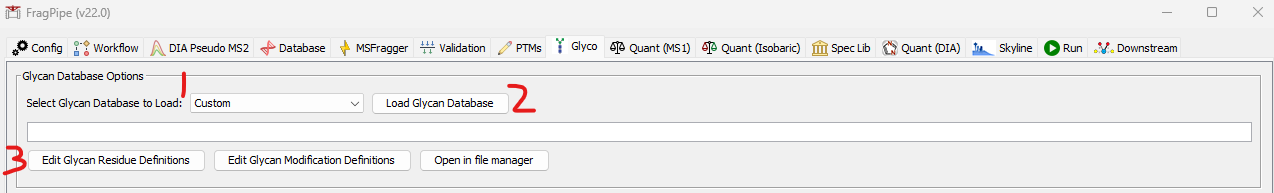
Glycan Database Glycans to search can be loaded on the Glyco tab. Use the Load Glycan Database button to load a list of glycans. The dropdown menu (1) can be used to select from several built-in default databases, or use custom to load your own database. NOTE: glycans vary considerably between organisms and, even in well studied organisms, not all glycans are known. Use the default glycan lists with caution and use your own glycan database if you know the specific glycans you are looking for! The glycans will be loaded to the appropriate parameter locations for MSFragger search (as mass offsets), PTM-Shepherd composition assignment, O-Pair localization, and Skyline output automatically.
Glycan database formats supported are Byonic, MetaMorpheus, and pGlyco-style glycans provided in a text file (one glycan per line). See example formats below. Glycan database files can be in .txt, .csv, .tsv, .pdb, or .glyc formats. If you have a different glycan database format that you would like to be supported, please contact us!
Byonic example: HexNAc(4)Hex(5)NeuAc(2)Fuc(1)
pGlyco example: (N(N(H(A))))
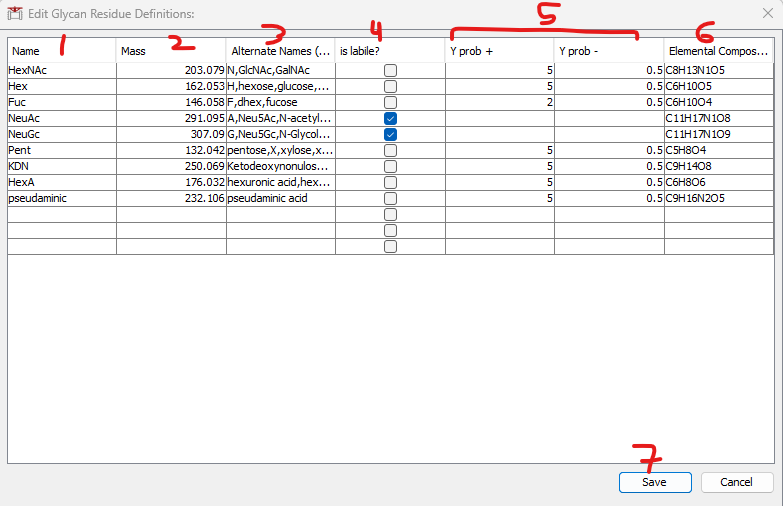
Glycans in the database file must be comprised of allowed “Glycan Residues” (monosaccharides) specified in the glycan_residues.txt file in FragPipe. To change the supported glycan residues, use the Edit Glycan Residue Definitions button (2). This will open the table pictured below for editing. NOTE: to load a glycan database successfully, all monosaccharides must be present in this table.
Editing the table:
1) Name: The name of the monosaccharide (whatever it will be called in the glycan database when it is loaded).
2) Mass: The monoisotopic mass of the monosaccharide.
3) Alternate names (optional): The default glycans are supplied with alternate names to facilitate parsing a variety of input formats. Use to allow parsing multiple different names for a glycan to the same Glycan Residue.
4) is labile?: Check this box if the monosaccharide is expected to dissociate completely from the glycan during collisional activation, and should not be observed on glycan Y ions. NOTE: if this box is checked, the Y prob +/- boxes are NOT required and should be left empty.
5) Y Prob +/-: Used for composition assignment in PTM-Shepherd. It is recommended to use the default values of 5 and 0.5, except leave blank for labile glycans.
6) Elemental Composition: the elemental (atomic) composition of the monosaccharide. Required for Skyline only.
Glycan modifications can be specified in a similar manner to glycan residues using the Edit Glycan Modifications Definitions button. All fields in the table are the same, except for the addition of “Required Residues,” which can be used to specify that a given modification can only be placed on glycans containing that residue (see default table for examples). These definitions will be populated to the glycan modifications options that are shown in a dialog window after loading a glycan database.
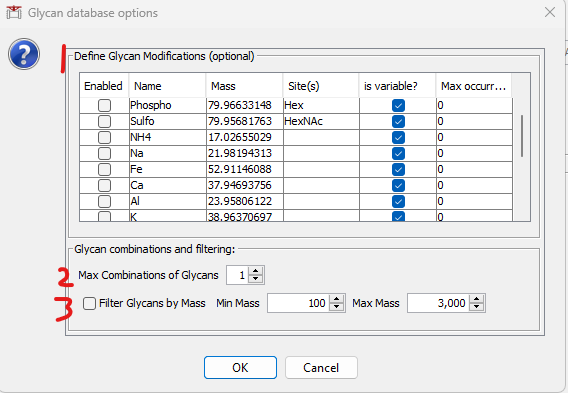
After loading a glycan database, the following window will be shown with 3 optional features. 1) to specify glycan modifications, 2) to generate combinations of glycans (e.g., for O-glycopeptides that may carry multiple glycans), and 3) to filter the loaded/generated glycans by mass (e.g., to exclude large glycans that are unlikely to be acquired by the mass spectrometer).
The modifications shown are what is present in the Glycan Modification Definitions table described above. To enable a modification, check the box at left. Modifications can be fixed or variable, and if variable, a maximum number per glycan can be specified. Note that if multiple types of modifications are enabled, combinations of them will be generated.
Customize the search settings
Glycoproteomics searches can require changes to parameters depending on the glycans being analyzed and fragmentation method used, in addition to the typical enzyme digestion/sample prep and instrument parameters that a standard proteomics search has. The key parameter changes for glyco searches are listed below, but for a full list/explanation of all parameters, see these pages: msfragger, philosopher
Basic Parameters - MSFragger
Set the mass tolerances, enzyme digestion, and variable and fixed modifications to appropriate values for your sample prep/acquisition. See the MSFragger parameter page here for details
Key Glyco Parameters:
- mass_offsets (list of glycan masses to search): (value: 0/mass1/mass2/…) All glycan masses to consider in a search should be specified as mass offsets (separated by ‘/’). NOTE: the default list is for mouse N-glycans (182 masses). Depending on the type of data and search, the glycans considered can vary. The masses of all glycans of interest should be determined and converted to a list separated by ‘/’ (see example parameter file). An arbitrary number of mass offsets can be searched, but search speed decreases with the number of masses used. If more than a few thousand masses are being considered, consider using an open search instead. For open searches, do NOT set any mass offsets.
- labile_search_mode: (possible values: nglycan, labile, off) nglycan mode checks for N-glycosylation motif N-X-S/T (X is not P), but is otherwise identical to “labile” mode. Labile mode should be used for all labile modifications (other than N-glycans), including O-glycans. Specify the allowed residues in restrict_deltamass_to. “Off” results in a standard (non-glyco) MSFragger search, in which all mass offsets are assumed to remain intact during activation.
- restrict_deltamass_to: (overridden in nglycan mode). Specify which amino acids (single letter codes) are allowed to contain the
glycan mass offsets. Allowed values are single letter amino acid codes.
Default value: ‘all’. For typical O-glycoproteomics searches, should be set to ‘ST’ or ‘STY’. In nglycan mode, this parameter is overridden to use the N-X-S/T sequon.
When labile_search_mode is ‘off’, ‘-‘ can be used to allow non-localized matches (i.e. matches to labile mods that have dissociated), by setting the value to ‘STY-‘, for example. It is not necessary to include ‘-‘ for labile and nglycan modes, as labile modifications are considered by default. - fragment_ion_series: fragment types of interest should be specified here depending on the activation method and data. Recommendations:
CID/HCD/IRMPD: b, y, Y (N-Glycans) or b, y (O-Glycans)
Hybrid (EThcD/etc): b, y, c, z, Y
ETD/ECD: c, z - remainder_fragment_masses: Specify partial glycan mass(es) to search that are retained on b/y fragment ions instead of complete loss of glycan. b/y ions retaining a HexNAc (called “b~/y~” in old FragPipe workflows). Multiple masses can be specified, but increased noise will decrease search sensitivity unless the remainder fragments are quite common. Recommended setting: 203.07937 for N-glycans (1 HexNAc remainder), none for O-glycans
- Y_type_masses: (value: 0/mass1/mass2/…) Masses of Y-type ions (intact peptide plus partially fragmented glycan) to consider in search. Note that ALL Y masses are applied to ALL potential glycopeptides (regardless of the actual glycan), so including too many can reduce search performance. Can be used in non-glyco searches as well (any modification that partially fragments, leaving behind some mass can be considered).
- diagnostic_fragments: (value: mass1/mass2/…) m/z values of diagnostic fragment ions (e.g., Oxonium ions) that appear in spectra of peptides containing a mod of interest. If diagnostic_intensity_filter > 0, at least one of the masses provided here must be found at sufficient intensity for any mass offset to be searched for the spectrum. To disable this checking, change diagnostic_intensity_filter to 0.
- diagnostic_intensity_filter: Minimum relative intensity (relative to base peak height) for the SUM of intensities of all diagnostic fragment ions found in the spectrum to consider this a potential glyco (or other labile mod) spectrum. Set to 0 to disable. A value of 0.1 means summed intensity must be 10% the height of the base peak in the MS/MS spectrum to be considered.
- localize_delta_mass: (values: 0 or 1) specifies whether to search for shifted ions (i.e., peptide fragments containing intact or partial glycan). Required to be set (1) for most glyco searches to allow glycans to be localized. Can safely turn off (set to 0) if HCD/CID search is not using any remainder fragment masses (no localization will be performed).
- deisotope: (values: 0 or 1) glycopeptides tend to be larger than tryptic peptides, making deisotoping very helpful. Recommended setting ‘1’ for glyco data.
Validation Parameters - Philosopher
The parameters for validation and FDR filtering in Philosopher are generally the same as open/offset searches. NOTE: Percolator can be used glyco searches but is not recommended. No modeling of probabilities for different glycans is currently done in scoring, potentially resulting in poor FDR control for less common glycans. Use with caution.
Key parameters that may change for Prophets/Philosopher are below:
- PeptideProphet: the –masswidth parameter must be larger than the largest glycan mass being searched (e.g., –masswidth 4000 is a common setting)
- PeptideProphet: specify “–glyc” flag for N-glycan searches to use N-X-S/T sequon in modeling
- ProteinProphet: set –maxppmdiff to a large value (e.g., 2000000) to prevent excluding proteins carrying glycans
Glycan Identification and FDR in PTM-Shepherd
MSFragger and Philosopher together report glycopeptides as a peptide sequence and a mass shift, and ensure that all such peptide-mass shift combinations reported pass the specified FDR levels. However, converting a mass shift to a specific glycan composition (or structure) is not always straightforward. In PTM-Shepherd, we have developed a glycan identification method that identifies the specific glycan composition in each glycopeptide-spectrum match and performs FDR filtering on the identified glycans.
Results will be written to the PSM table with the assigned glycan in the Observed Modifications column, score in the Glycan Score column, and q-value (FDR) in the Glycan q-value column. NOTE: PSMs that did not pass glycan FDR are still listed, and must be filtered by Glycan q-value less than the set FDR. Glycans are also written to the Assigned Modification and Modified Peptide columns if the PSM passed glycan FDR. The default behavior is to subtract the mass of the glycan from the listed delta mass when writing the assigned glycan to the Assigned Modification column, however, this prevents re-running the glycan assignment on the same results table and can be disabled in the advanced settings if desired.
Default parameters for N-glycan analysis are shown below along with a description of each parameters.
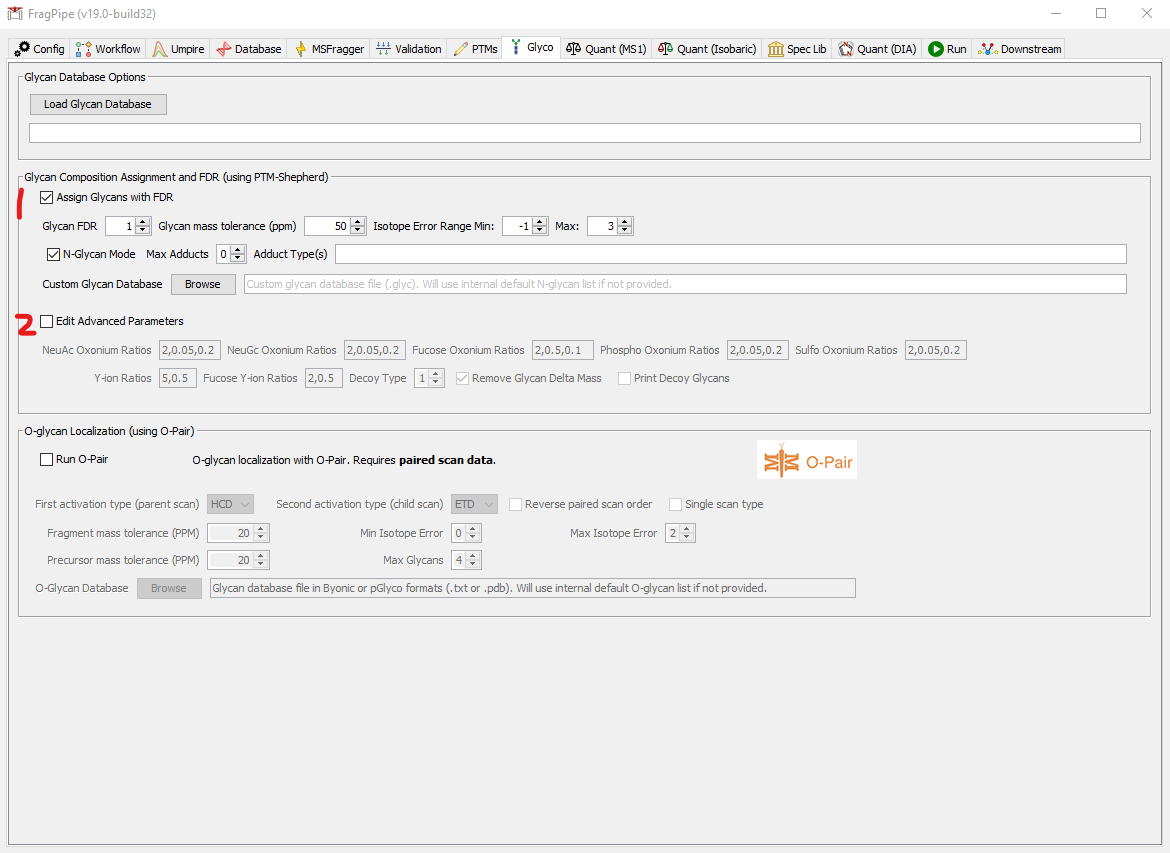
- Glycan Assignment and FDR: basic parameters
- Check the box to enable glycan assignment. NOTE: this is currently only supported for mass offset searches, not for fully open searches.
- Glycan FDR: specify the desired glycan FDR. PSMs will have the resulting q-value written to the PSM table. NOTE: PSMs that fail glycan FDR will NOT be removed from the PSM table, but can be filtered by looking for PSMs with “Glycan q-value” less than the FDR set here. Glycan FDR filtering is performed after PSM/peptide/protein FDR (done in Philosopher).
- Glycan mass tolerance (ppm): Tolerance for matching between the mass of a candidate glycan and the observed delta mass (ppm)
- Isotope Error Range: Precursor monoisotopic peak selection errors to consider when matching candidate glycans, ranging from min to max. Typically should be set relatively wide as matches with unlikely errors are penalized in scoring unless there is fragment-ion strong evidence.
- N-glycan mode: Check for N-glycans. Sets allowed positions to be N-X-S/T sequon only and sets default glycan database to N-glycan internal list. If unchecked, allowed site(s) are taken from the “Restrict localization to” box in the main PTM-Shepherd settings above.
- Max Adducts: If considering non-covalent adducts (e.g., ammonium), set the max number of adducts allowed on a glycopeptide here. Set to 0 to disallow adducts.
- Adduct Types: Allowed adduct types: NH3, Fe3, Fe2, Na, Ca, Al. Note that NH3 refers to an ammonium adduct (NH4+). All adducts replace protons equivalent to their charge state (e.g., Fe3 replaces 3 protons as Fe 3+)
- Custom Glycan Database: Provide a custom list of glycan candidates to match as a text file (.txt or .glyc). File format: one glycan per line, glycans can be provided in Byonic format “Residue1(Count1)Residue2(Count2)… % Mass” or “Residue1-Count1_Residue2-Count2…” where “Residue” is one of HexNAc, Hex, Fuc, NeuAc, NeuGc, Phospho, or Sulfo, “Count” is the total count of that residue in the glycan composition, and “Mass” is the total glycan mass (NOTE: mass is optional - it is provided in the Byonic format, but only the composition is necessary to read the glycan database, so mass can be skipped if generating the file manually). An example glycan database file is provided here as a template:
- Advanced Glycan Parameters:
- Check the box to enable editing advanced parameters. These are the likelihood ratios used to compute glycan scores and may need to be changed for fragmentation other than HCD or for O-glycans.
- Oxonium ion ratios: For each category of oxonium ions (NeuAc, NeuGc, Fuc, Phospho, Sulfo), oxonium ions specific to glycans containing this residue increase the score by log of the first value if found, and decrease it (by adding the log) of the second value if not found. The first value thus should always be greater than 1 and the second value always less than 1 (but must be greater than 0). The third value is the “expected” intensity (relative to the base peak of the spectrum) of such oxonium ions, used to decrease the effect of oxonium ions from co-fragmentation of another glycopeptide. Oxonium ions found at values less than the expected intensity will have their positive contribution to score decreased, while ions found above the expected intensity will have their positive contribution increased.
- Y ion ratios: Y-ions are divided into two categories: containing Fucose or not. Likelihood ratios are the same as for oxonium ions, but no expected intensity is used.
- Decoy Type: Several methods of decoy generation are available, but the default (1) should be used in most situations. 0 means generate decoys with intact mass within +/- 3 Da of the target glycan mass, resulting in less strict FDR filtering (generally not advisable). 1 means generate a decoy mass within the provided mass tolerance of the target glycan mass, allowing a randomly selected isotope error. 2 is the same as 1, but without isotope error. 3 means decoy glycan masses are exactly the same as targets and the mass error is not used in distinguishing between targets and decoys.
- Remove Glycan Delta Mass: If checked, removes the glycan delta mass from the PSM table when the glycan is assigned and written to the assigned modifications column. Default is enabled. Required to allow IonQuant to trace peaks (and for the reported masses and modifications in the PSM table to remain consistent). NOTE: delta mass removal means that the PSM table must be regenerated prior to re-running PTM-Shepherd on the same results table.
- Print Decoy Glycans: By default, if a PSM matches to a decoy glycan, the best target glycan is reported in the PSM table with a q-value of 1. To report the decoy glycan instead for diagnostics, check this box.
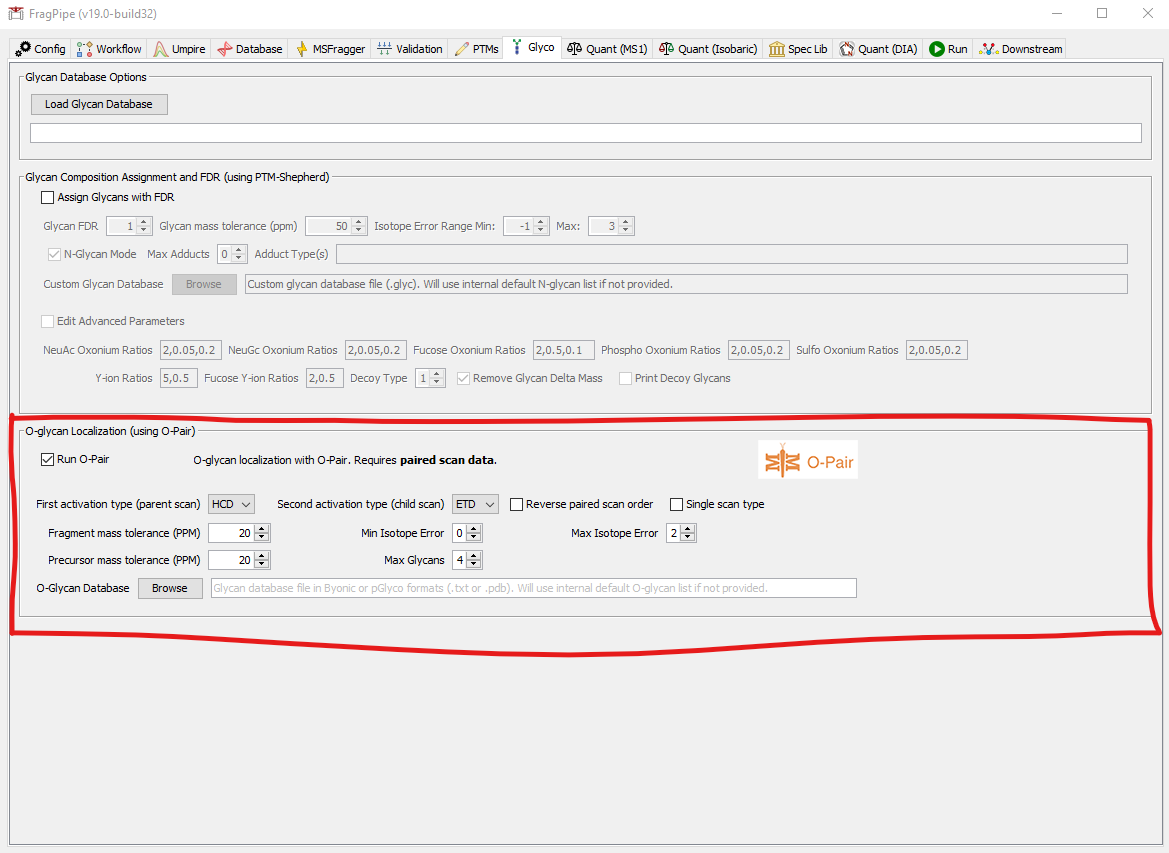
O-Glycan Localization with O-Pair
O-Pair search can deconvolute and localize multiple O-glycans on a peptide using an electron-based activation MS2 scan. The O-Pair FragPipe workflow uses MSFragger to identify the peptide from a collisional activation scan (by default) and O-Pair to localize the glycan(s) using the paired electron-based activation scan of the same precursor.
Note: O-Pair requires .NET Core 6.0 to be installed on your computer. You can download it from here.
Parameters:
- Check the box to enable O-Pair search
- First activation type (parent scan): First scan of the precursor. Usually this is the collisional activation scan, but it does not have to be.
- Second activation type (child scan): Second scan of the precursor. Usually this is the electron-based activation scan, but it does not have to be.
- Reverse paired scan order: Check this box if the electron-based activation scan comes before the collisional activation scan
- Single scan type: Check this box if using EThcD data without paired scans. MSFragger search settings need to be adjusted to search EThcD data, and the same scan will used as its own “pair” for O-Pair localization.
- Fragment mass tolerance (PPM): MS2 tolerance in PPM
- Precursor mass tolerance (PPM): MS1 tolerance in PPM
- Min isotope error: Defines range of precursor monoisotopic peak assignment errors allowed (from min to max)
- Max isotope error: Defines range of precursor monoisotopic peak assignment errors allowed (from min to max)
- Max Glyans: (key parameter) the maximum number of glycans to attempt to localize on a single peptide.
- O-Glycan Database: The list of glycans to be used for localization. Will be set automatically when using the Load Glycan Database button at the top of the Glyco tab.
Set the output location and run
On the Run tab, make a new folder for the output files (e.g. ‘glyco_results’), then click ‘RUN’ and wait for the analysis to finish.
When the run is finished, ‘DONE’ will be printed at the end of the text in the console.
Examine the results
In the output location, you will see several output files including the “psm.tsv” table, which contains all PSMs found in the analysis. For searches without quantitation, the PSM table is the best place to look for glycopeptide information.
Visualizing Glycopeptide Spectra: new in 18.0
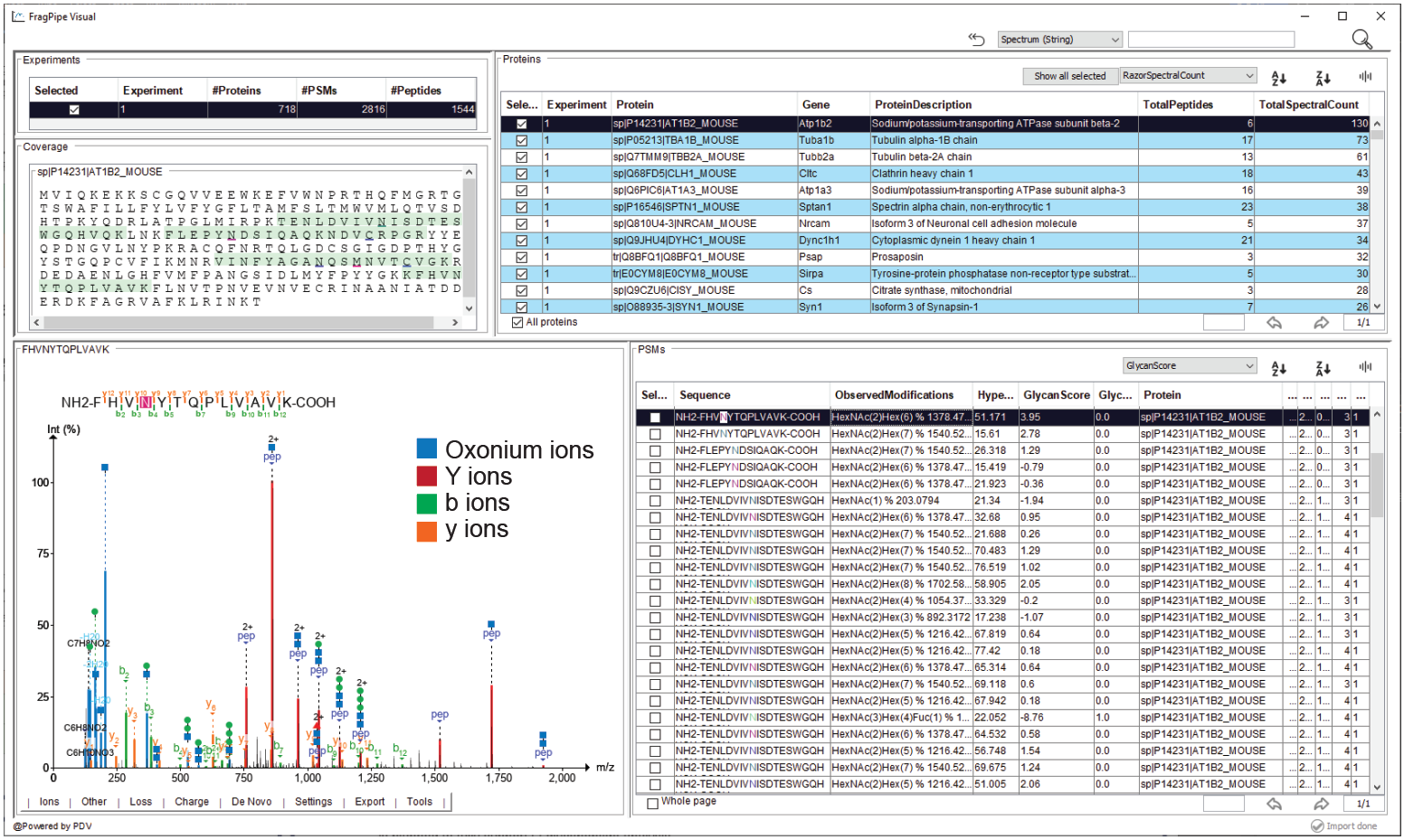
The spectrum viewer can be accessed from the “Open visualization window” button on the Run Tab in FragPipe. This will open the viewer software using the PSM table and spectrum file manifest from the folder currently specified at the top of the run tab. NOTE: to view spectra from old runs/results, simply change the output directory on the run tab to the folder containing the results table you’d like to view.
The viewer displays an experiment-level summary of PSM/peptide/protein counts and protein table + coverage map in the top panel. The bottom panel displays the PSM table at right and selected spectrum at left. To view glycopeptide spectra, glycan-specific fragment ions can be enabled using the “glycan: …” options in under the “Other” menu in the spectrum. Glycan fragments (glycan B/Y ions) and peptide backbone fragments that have lost all of the glycan or retain a single HexNAc residue can be viewed in the spectrum, as in the example below. It is also possible to define custom glycan remainder masses to annotate in the spectrum and various other useful tools - for a complete guide to the visualization tool, see the associated tutorial.
Skyline: new in 22.0, improved in 23.0
As of FragPipe 23.0, DDA and DIA glycoproteomics results can be automatically visualized in Skyline by checking the “Generate Skyline Document” box on the Skyline tab.
Let Skyline override peak bounds: Enable this checkbox to have Skyline override the peak bounds from IonQuant (DDA) or DIA-NN (DIA) and reintegrate all peaks. Disable to see the bounds used for quantification in FragPipe (this is the default setting).
Special Modifications Mode: set to N-glyco or O-glyco depending on the analysis
The PSM Table: Key columns for GlycoPSM information
If NOT using Glycan Assignment in PTM-Shepherd or O-Pair localization:
- Delta Mass: column contains the glycan mass observed. Since no composition assignment is performed, this is the place to look for glycoPSMs.
- NOTE: glycans will NOT (generally) be written to Assigned or Observed Modification columns in this case
- MSFragger localization column is the same as if using glycan assignment in PTM-Shepherd.
If using Glycan Assignment in PTM-Shepherd:
- Total Glycan Composition: contains the assigned glycan composition from PTM-Shepherd
- Assigned Modifications: the mass and location glycan assigned will also be written to the Assigned Modifications column by PTM-Shepherd to enable processing by quant tools.
- Glycan Score: contains the score associated with the glycan composition (higher is better). Scores may be negative, particularly if using higher energy fragmentation that reduces the number of glycan fragment ions present.
- Glycan q-value: contains the q-value (FDR) associated with the glycan assignment. Use this column to filter glycoPSMs to a desired FDR level (e.g., q < 0.01 for 1% FDR)
- MSFragger localization: contains the localized site of the glycan if localize_delta_mass was enabled in MSFragger. Peptide sequence is printed in capital letters with the determined location as a lower case letter. If multiple locations are possible (ambiguous localization), multiple residues may be lower case. NOTE: in cases of ambiguous localization, when writing glycans to assigned modifications for quantitation, the first allowed site will be used as the site for site-level quantitation.
If using O-Pair localization:
- Assigned Modifications: the mass and location of glycans found by O-Pair will be written to Assigned Modifications to allow for quantitation of glycopeptides. NOTE: unlocalized glycans will be placed on the first available site. Use the Confidence Level column to filter confidently localized glycans.
- O-Pair Score: Localization score from O-Pair
- Number of Glycans: Number of glycans on the peptide determined by O-Pair localization
- Total Glycan Composition: Summed composition of all glycans present at all sites
- Glycan Site Composition(s): The compositions of individual glycans determined by O-Pair (H=Hex, N=HexNAc, A=NeuAc, etc.)
- Confidence Level: Confidence in the localization for this PSM. Level 1 means all glycans localized, Level 1b means all glycans localized by process of elimination (rather than direct fragment ion evidence), Level 2 means some glycans localized but not all, Level 3 means no glycans localized.
- Site Probabilities: Each localized glycan is shown here in the format (position, composition, probability). Position refers to position in the peptide, composition is the monosaccharide makeup, and probability is the O-Pair localization probability for that glycan.
- 138/144 Ratio: ratio of 138 to 144 oxonium ions, can be useful for distinguishing types of glycans
- Paired Scan Num: The PSM table shows the information (scan number, RT, etc) of the collisional activation scan. The Paired Scan Num column shows the scan number used for localization by O-Pair.
Quant Reports:
IonQuant: If enabled, IonQuant will read assigned glycans from PTM-Shepherd and use for LFQ analysis. Glycan information will be saved to peptide/protein summary tables for each experiment.
TMT-Integrator: If performing TMT analysis, reports summarizing the TMT results can be found in the “tmt-report” folder. For glyco searches, the multi-mass reports summarize the results by peptide sequence and glycan composition. All other reports are as in typical searches (see this page for details). TMT-reports can be loaded directly into many downstream analysis tools (such as Perseus) for further analysis.